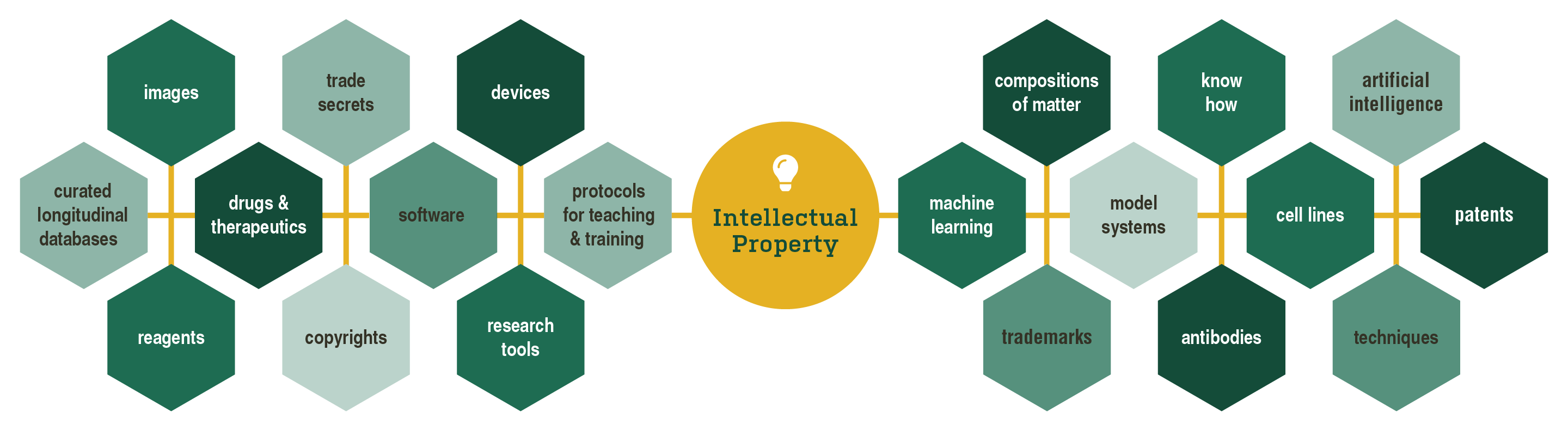
Looking to learn about different kinds of intellectual property?
Here's what you need to know. Scroll down to read more about the various types of IP.
Definitions for different types of IP:
Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies have commercial value as research reagents, in diagnostic assays, and in therapeutic applications. Polyclonal antibodies also have potential value when large quantities of sera are available.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science dealing with the simulation of intelligent behavior in computers. It is a broad and rapidly advancing field that includes machine learning, deep learning, and reactive AI. As software, it is typically covered under copyright protection.
Cell Lines
Defined populations of cells that can be maintained in culture for an extended period, retaining stability of certain phenotypes and functions. Examples include hybridoma cell lines and iPSCs. They can also include cell lines that have been developed for an assay/readout.
Compositions of Matter
A material synthesized, identified or constructed from multiple components that together exhibit some sort of emergent property. Examples include novel chemical compounds, antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates.
Copyrights
A copyright is an original work of authorship fixed in a “tangible means of expression,” such as when it is written on paper and printed in books or recorded via audio or video. Software is typically protected by copyright, though sometimes it can also be protected by patents. Videos, books, music, etc. are other examples of Intellectual property that are protected by copyright.
Curated Longitudinal Databases
Patient data collected from multiple sources are selected, organized, and presented in a user-friendly way for downstream analysis, therapeutic development, or treatment decision making. While novel data collection and curation methods can be patent protected, contents within the curated database are protected by copyright.
Devices
Any piece of equipment designed to serve a particular purpose or perform a particular function, medical or otherwise. Examples of protectable inventions in this area include both new devices and improvements to existing devices, such as a modified surgical instrument with added functionality or a modified dental implant with improved durability.
Drugs/Therapeutics
Methods or substances used for treating diseases or to change one’s physiology or psychology. Examples include insulin for diabetes, chemotherapeutics for cancer, immunotherapies for inflammation, etc.
Images
A kind of intellectual property protected by copyright. UAB has a repository of histopathology images that are routinely licensed to publishers of textbooks.
Know-how
Scientific and factual knowledge not covered by a patent but considered useful by a licensee to practice a patent.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence in which a machine learns from a training dataset and adjusts its output based on that data. Facial recognition, voice recognition, and the algorithm that controls what advertisements you see on social media all rely on machine learning.
Model Systems
Organisms or other self-contained systems used to evaluate a particular biologic activity or disease process, e.g., a mouse model designed to study cystic fibrosis.
Patents
A type of intellectual property that confers the exclusive right to the patent owner to exclude others from practicing that invention. As an example, see compositions of matter.
Protocols for Teaching & Training
These are automatically copyrighted when written down and sometimes can be licensed to other academic centers or institutes. For example, scales developed by physicians or scientists to measure the baseline or progress of patients after therapy can be of commercial value.
Reagents
Substance or mixture used in chemical or biological reaction and analysis, e.g., buffer formulations in assay development.
Research Tools
Research tools are assets generated by university employees that are intended to aid in research but are not necessarily patentable. The most common examples are cell lines, antibodies, and genetically modified model organisms. Although the patentability of these is limited, they still hold significant commercial value.
Software
A computer program or component thereof, including software applications. Examples might include software designed to provide additional functionality for an electronic medical record or a smartphone app supporting gamification of educational objectives.
Techniques
Specialized method involving skill and knowledge to execute a task. Examples include statistical methods or algorithms for analyzing datasets, the ability to isolate and grow primary cells or the ability to crystallize a protein.
Trade Secrets
Trade secrets are practices and processes that give a company an advantage over its competitors because they remain undisclosed to the public (held as secret). An example is the formula for making Coca Cola®.
Trademarks
Name, symbol, or visual imagery used to identify intellectual property or company products. For example, a car logo. Trademarks need to be registered to prevent copying or misuse.

Disclose Your Invention
Now that you have a better understanding of the different types of IP, you can disclose your invention.

Contact Us
More questions? No problem. Just contact our staff and we'll be here to help.

Inventors' Guide
Want more in-depth info about intellectual property, or want to read about the process of commercializing your invention? Check our Inventor's Guide (PDF).