Case History
A 45 YO F with PMH of RA-associated bronchiolitis on oral prednisone, presented with F, SOB, cough, night sweats, and oral lesion. Few days later she developed acute abdominal pain. CT revealed pneumatosis along with free air. An exploratory laparotomy revealed a perforation in jejunum.
What is the best answer?
- Perforated jejunum 2nd to SCD
- Perforated jejunum 2nd to IBD (CD)
- Perforated jejunum 2nd to Histoplasmosis
- Perforated jejunum 2nd to RA
Answer: C. Perforated jejunum 2nd to Histoplasmosis
Discussion:
Histoplasmosis is the most prevalent endemic mycosis in the United States and most commonly occurs in the southern and mid-western states. The majority of cases of histoplasmosis are asymptomatic pulmonary infections. In endemic areas, the vast majority of infections are clinically silent, but may cause serious disease including acute pulmonary disease and disseminated disease involving multiple organ systems, including the gastrointestinal tract. Within the gastrointestinal tract, the most commonly involved sites are the terminal ileum and proximal colon, but can be seen throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis most commonly results in stenosis or ulcerations, but can, less commonly, result in life-threatening perforations which can be fatal.
Histoplasma is a saprophyte that exists in the mycelial form in nature. Majority of infections are asymptomatic in immunocompetent hosts but clinical disease is common in immunosuppressed patients
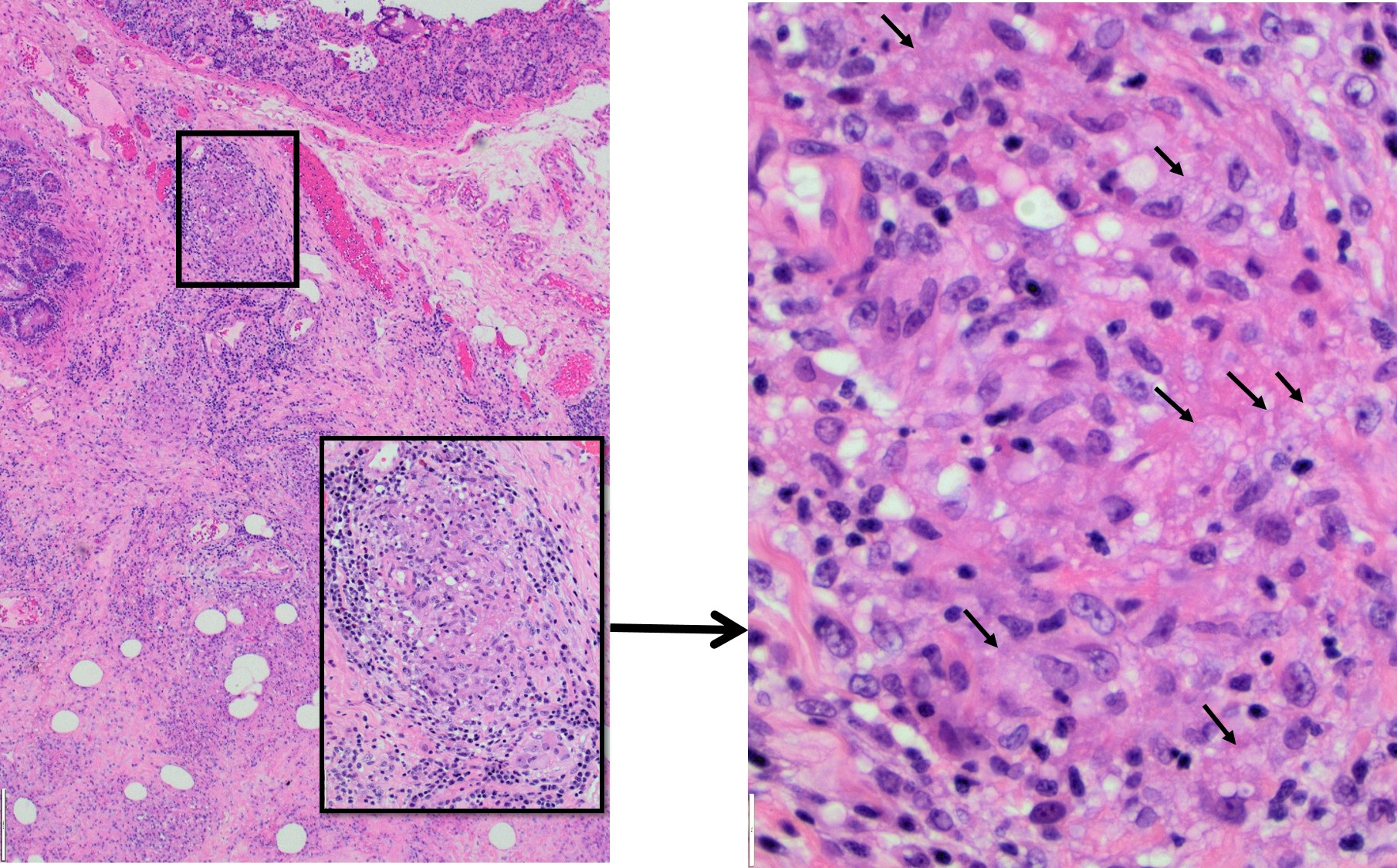
Histological examination of surgical specimen showed granulation tissue, transmural chronic inflammation, and multiple non-necrotizing granulomas. This makes Chron’s disease one of the main differential diagnosis. However, the mucosal epithelium did not show chronic changes, such as dense lymphoplasmacytic inflammation in the lamina propria, basal lymphoplasmacytosis nor architectural distortion. No cryptitis or crypt abbesses were observed which are usually present in active CD.
On the other hand, intracellular small yeast within histiocytes, lymphoid hyperplasia, infiltrates of eosinophils, neutrophils, necrotizing granulomas are the classic findings of histoplasmosis. A GMS special stain for fungi in our patient showed numerous micro-organisms confirming the diagnosis.
