Case History
A 61-year-old female with erythematous vulvar lesion and previous history of invasive high-grade utothelial carcinoma.
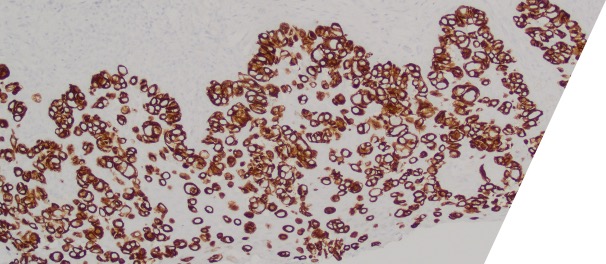
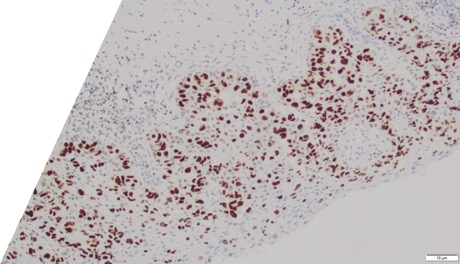
What is the diagnosis?
A. High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL/VIN3)
B. Extramammary Paget Disease
C. Melanoma in situ
D. Secondary involvement by previous known adenocarcinoma
Correct answer: D. Secondary Paget Disease
Discussion: Secondary Paget Disease
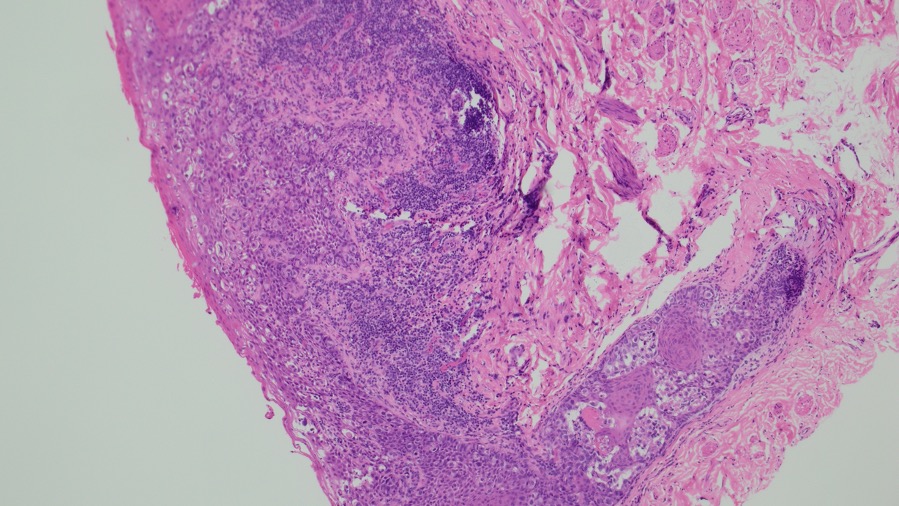
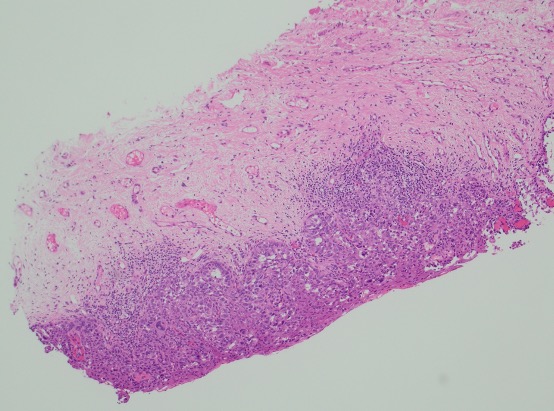
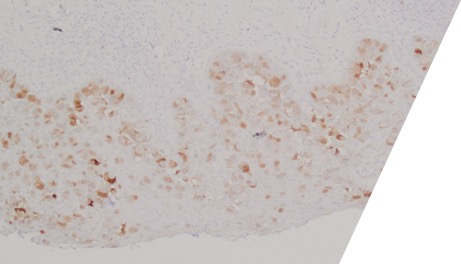
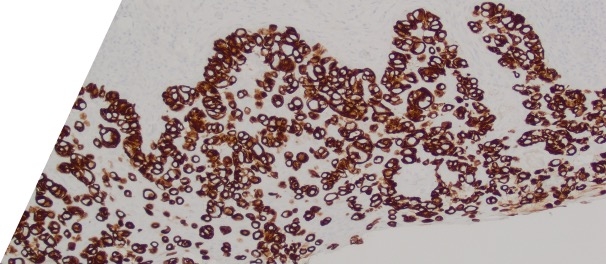
Large round malignant cells with pale cytoplasm and enlarged nucleolus and prominent nucleoli are present within the epidermis. The cytoplasm contains mucin. Differential diagnosis include HSIL, Paget disease (primary or secondary), and melanoma in situ. The lesional cells are strongly positive for CK7, CK20, CAM5.2 and GATA3, scattered positive for p63; and patchy staining for p16, negative for ER and SOX10. High-risk HPV-ISH is negative.
Patient's history of invasive high-grade urothelial carcinoma is shown. The tumor cells showed similar morphological features to the tumor cells in current specimen. The findings are compatible with secondary involvement by previously diagnosed urothelial carcinoma.
Due to morphological similarity both architecturally and cytologically, precise diagnosis based on H&E alone can be challenging, and IHC can be overlap. The current case highlight the importance of clinical history in establishing an accurate diagnosis for patients with an extension of urothelial carcinoma into the GYN tract.
Case contributed by: Hua Guo, M.D., M.S., Associate Professor, Breast Section Head, UAB Pathology