UAB's Geographic Information System (GIS) is a tool that assists in plotting and analyzing geographical data and is useful in decision-making processes across fields like urban planning, environmental management, and business logistics.
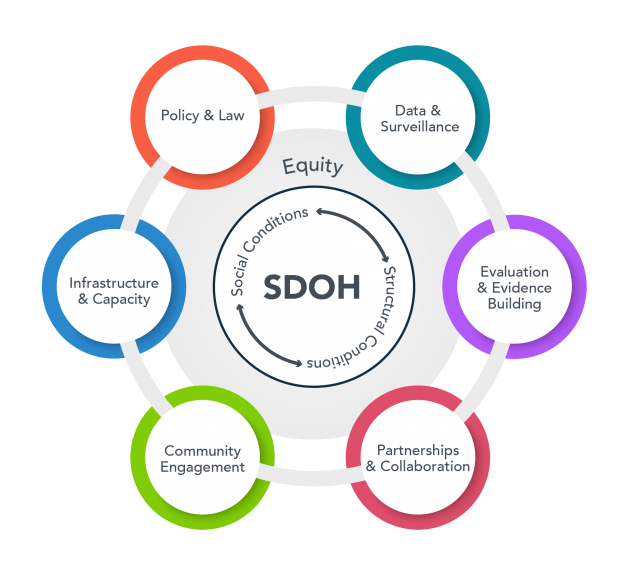
The Social Determinants of Health (SDH) Core empowers UAB investigators to evaluate how social and environmental factors influence the onset, development, management, and outcomes of diseases. It also promotes the development of interventions that mitigate these factors.
By combining integrated data, methodologies, and expertise from various fields such as social science, spatial and environmental science, clinical and translational science, genomics, informatics, and epidemiology, we pave the way for pioneering investigations into the genome-sociome-exposome pathways linked to health and disease.
The Core is dedicated to augmenting research on the social determinants of health, aiding teams as they study the conditions dictating people's birth, living, working, and aging environments.
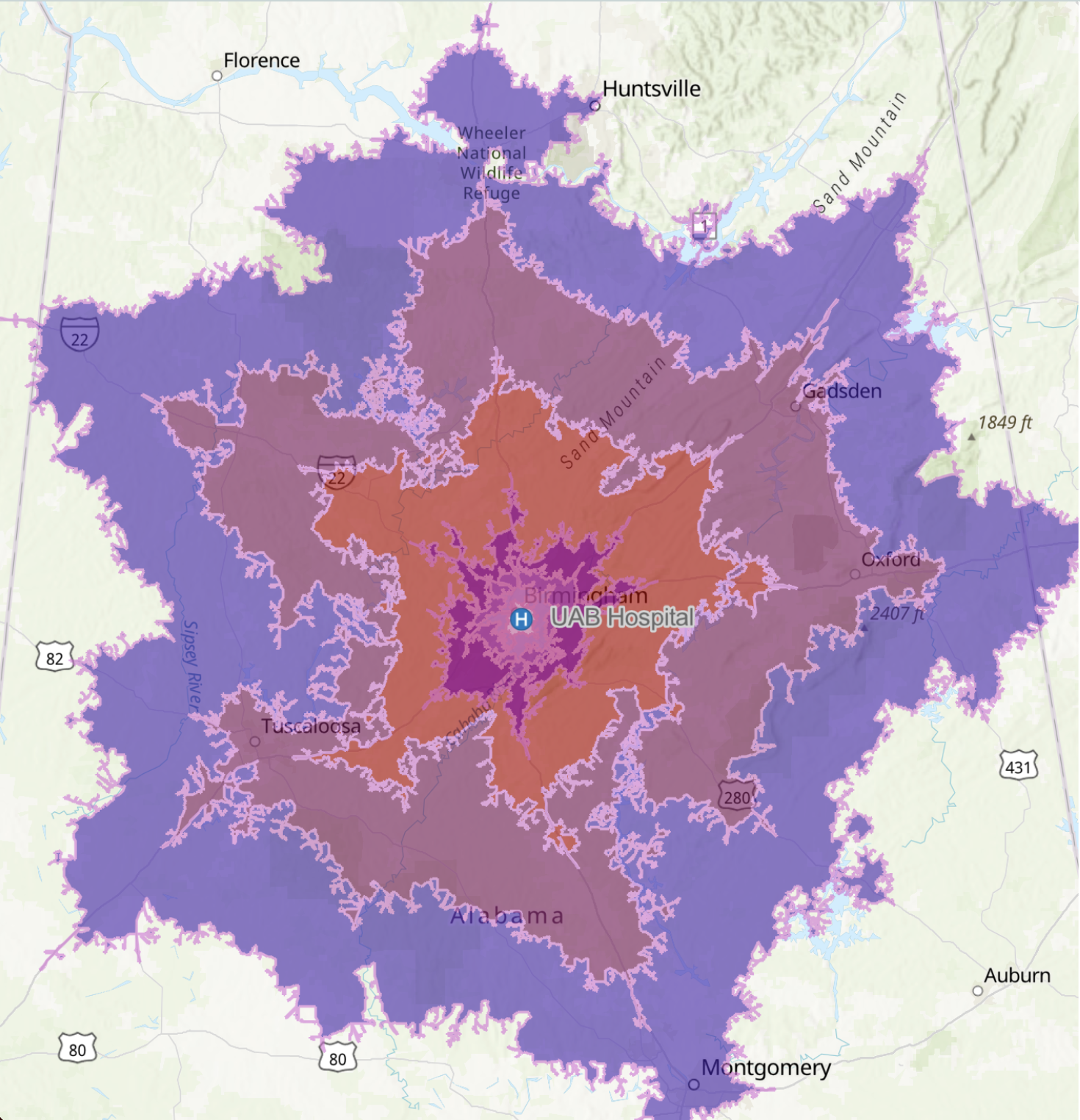
The UAB GRID (Geospatial Research and Information Domain) (GRID) is a type of Geographic Information System (GIS) that not only plots data on a map but also analyses the information regarding what things are and where they are located. Used across various industries, GIS helps in understanding patterns, relationships, and geographical contexts, thereby enhancing communication, decision-making, and efficiency.
GIS software enables the creation, editing, and analysis of maps, assisting in answering questions about location, proximity, relationships, and changes over time. It's a tool employed in diverse fields, including environmental management, urban planning, emergency response, and business logistics.
However, GIS isn't just a mapping tool. It offers a more dynamic understanding of the world, aiding in informed decision-making by translating complex data into a more comprehensible visual format.